How to Run PowerShell or Command Prompt as Administrator in Windows?
Solution 1
1. Click on the Start button or Search and enter CMD or PowerShell;
2. On available items, Right Mouse Button click and select Run as administrator.
Solution 2
1. Press Ctrl+Shift+Escape at the same time. Task Manager windows will appear;
Or
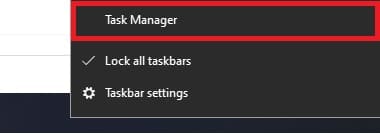
1. Right Mouse Button click on the taskbar and select Task Manager;
Or
1. Press Ctrl+Alt+Delete at the same time and click on Task Manager
2. In Task Manager navigate to File\Run new task;

3. In the new window select Create this task with administrative privileges, enter CMD or PowerShell, and click OK;

NOTE: IF you enter powershell ise, then run PowerShell ISE, by default (powershell) runing PowerShell console.
Solution 3
1. Navigate to folder, where stored *.exe files;
Command Prompt (CMD):
C:\WINDOWS\system32\cmd.exeWindows PowerShell:
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exeWindows PowerShell ISE:
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell_ise.exeNOTE: There are also powershell.exe.xml and powershell_ise.exe.xml, don’t run them, run files with PowerShell icons.
2. Right Mouse button click at *.exe file and select Run as administrator.
Solution 4
If you use Windows 10 release 1703 and above:
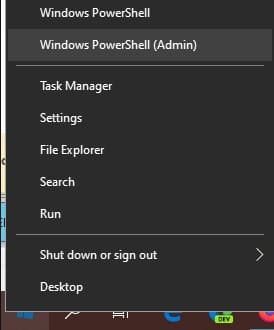
Right Mouse button click on Start button and select Windows PowerShell (Admin);
NOTE: In Windows Server available Command Prompt is like in Windows 1607 and above. Also, you replace Windows PowerShell with Command Prompt in Windows Settings.
If you know other solutions – let me know in the comments.