Hyper-V Virtual Disk Operations: Compact, Convert, Expand, and Shrink – How to Guide and Tips.
Compact
1. Run your Hyper-V Manager and click on Edit Disk;

2. Click Next;
3. Click on Browse to select your disk for operations;
4. After Disk is selected click Next;

5. First option is Compact (this is the simplest operation). Click Next;

6. At the next page click Next;
Convert
1. Option Convert (change your Virtual Disk format, *.vhd or *.vhdx). Click Next;

2. Select the format and click Next;

3. Select the type of Virtual Disk.
NOTE: In enterprise is Best Practice – to use a Virtual Disk type Fixed size.
4. Make a choice and click Next;

5. Click on Browse to select the final name and destination of Virtual Disk, and click Save;
7. If it’s ok – click Next;
8. Click Finish to run this operation;
Expand
1. Run Hyper-V Manager and click on Inspect Disk and select target Virtual Disk to show information about it. Click the Close button;
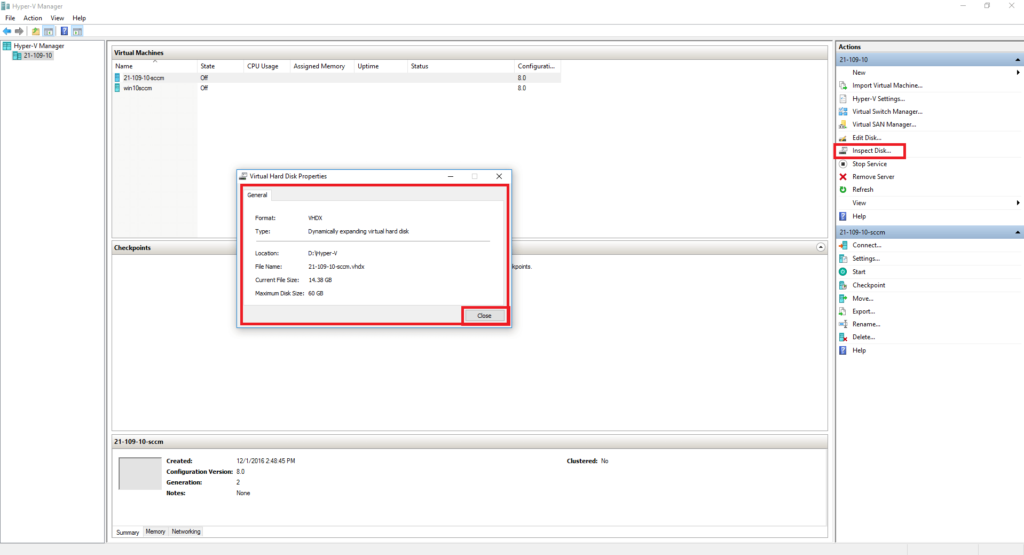
2. We have 60 GB VHDX, Expand it. Click on Edit Disk in Hyper-V Manager; Click the Next button;
3. Click the Browse button and select target Virtual Disk;
4. After selecting click the Next button;

5. Select Expand option and click the Next button;

6. Enter the new size and click the Next button, I’m set to 80 GB. (You must have free space to do this);

7. Check the final information and click the Finish button;
8. Let’s Inspect Disk again. As we see – it now 80 GB size.

9. Connect to VM, which Virtual Disk we Expand. Login in (user must have Local Administrator Rights) and open This PC;
10. As we see it’s 60 GB (old size) but not 80 GB. Close This PC. Right Mouse Button click on the Start button and select Disk Management;

11. After the Disk Management console opens you will see Unallocated space on the Disk (20 GB);

12. Right Mouse Button click on Disk “(C:)” and select Extend Volume;

13. Click the Next button;

14. It shows up space for extending. Click the Next button;

15. Click Finish to apply changes;

16. As we see – The disk is extended to 80 GB, close the Disk Management console;

17. Open “This PC again. Hooray “Local Disk (C:)” now has an 80 GB size.

Shrink
1. Run Hyper-V Manager and make sure your Virtual Machine (VM) with target “Virtual Disk is in an Off state. Close Hyper-V Manager;

2. Open Disk Management on the Hyper-V computer (local pc). Right Mouse Button click on the Start button and select Disk Management;

3. After the Disk Management console opens, go to the upper menu. Click Action and then Attach VHD;

4. Click Browse to select the target Virtual Disk file;

5. After selecting click the OK button;

6. We connected Virtual Disk;

7. Right Mouse Button click on the connected Disk and select Shrink Volume;

8. Enter the size in MB (Megabytes) to shrink from Disk. Click the Shrink button;

9. Perfect, shrinking is successful;

10. Right Mouse Button click on your Virtual Disk and select Detach VHD;

11. Click OK and close the Disk Management console;

12. Run your Hyper-V Manager and click on Edit Disk;

13. Click the Next button;

14. Click the Browse button to select target Virtual Disk;

15. After selecting Disk click the Next button;

16. As you see we get a new option Shrink, select it and click the Next button;
NOTE: Option “Shrink” is available if “Virtual Disk” has “Unallocated” space.

17. Enter the new size and click the Finish button;

18. Inspect our Virtual Disk again, now it’s 41 GB;

19. In the system;